
BSc, PhD(Liv), DSc(Aberd), CChem, FRSC (Emeritus Prof, former HoD)
Emeritus Professor
- About
-
- Email Address
- m.d.ingram@abdn.ac.uk
- School/Department
- School of Natural and Computing Sciences
Biography
- Fellow of the Society of Glass Technology since 2000: since 1999, Editor of “Physics and Chemistry of Glassesâ€: European Journal of Glass Science and Technology, Part B .
 - Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts in 2002 and in the same year awarded a Research Prize by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation to become Project Leader within Sonderforschungsbereich 458 and Visiting Professor at the University of Münster.
 - Interests include electrochemical energy storage, and the historical aspects of glass science and its impact on society and the environment.
- Research
-
Research Overview
Physical Chemistry of Glasses
Ion Transport Processes
Much research today is concerned with ion transport across a wide range of materials including glasses, molten salts and polymer electrolytes. Optimising ion mobilities in these materials is vital for the development of new electrochemical power sources (including advanced batteries and super-capacitors for use in electrical vehicles or laptop computers), while there is a compelling need for reducing ion mobility in glasses used as electrical insulators or indeed in the storage of nuclear wastes.
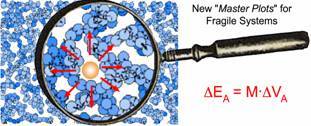
My own research is focused on identifying the microscopic mechanisms of ion transport (see the graphic) using a variety of techniques, including:
- variable-pressure, variable temperature (VPVT) impedance spectroscopy (IS)
 - high-pressure differential scanning calorimetry (HPDSC)
 - VPVT radioactive tracer studies of cation diffusion, with Profs. K Funke and H. Mehrer, Univ. of Münster, Germany
 - positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS), with Dr.A.J. Hill, CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia
Economic and environmental factors drive this research forward. These include the need to find ways of storing electricity generated by wind farms, where huge currents are involved, and to find reliable replacements for nickel-cadmium and lead-acid storage batteries, whose disposal is clearly problematic. Our strategy is to focus on basic science and to identify the barriers to ion motion in new materials, which include brittle glasses, rubbery polymers and spongy gels. We report (references 5 and 10) a new equation, EA = M.VA, which enables us to calculate the heights of the above-mentioned barriers in a wide range of materials.
- variable-pressure, variable temperature (VPVT) impedance spectroscopy (IS)
- Publications
-
Page 1 of 1 Results 1 to 24 of 24
A new polymer electrolyte based on a discotic liquid crystal triblock copolymer
Electrochimica Acta, vol. 93, pp. 279-286Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.01.060
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/5846/1/Imrie.pdf
New insights from variable-temperature and variable-pressure studies into coupling and decoupling processes for ion transport in polymer electrolytes and glasses
Solid State Ionics, vol. 196, no. 1, pp. 9-17Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2011.05.019
Pressure dependance of the ionic conductivity of Na- and Na-Rb borate glasses
Solid State Ionics, vol. 177, no. 11, pp. 963-969Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2006.03.009
Evidence from infrared spectroscopy of structural relaxation during field assisted and chemically driven ion exchange in soda-lime-silica glasses
Physics and Chemistry of Glasses, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 84-89Contributions to Journals: ArticlesFree volume anomalies in mixed-cation glasses revealed by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS)
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 1620-1623Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b419201j
Free volume and conductivity in polymer electrolytes
Electrochimica Acta, vol. 50, pp. 3955-3962Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.058
‘Activated’ polypyrrole electrodes for high-power supercapacitor applications.
Solid State Ionics, vol. 169, no. 1-4, pp. 51-57Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2002.12.003
'Ladder-doped’ polypyrrole: a possible electrode material for inclusion in electrochemical supercapacitors?
Journal of Power Sources, vol. 129, no. 1, pp. 107-112Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.11.005
Discotic side group liquid crystal polymer electrolytes
Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, vol. 408, pp. 33-43Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/1542140049025801
Ionic conductivity of a fragile glass-forming molten salt: Modelling it dpendence on frequency, temperature and pressure.
Z. Metallkd, no. 95, pp. 921-927Contributions to Journals: ArticlesSignificance of activation volumes for cation transport in glassy electrolytes.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, vol. 6, no. 13, pp. 3659-3662Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b314879c
What variable-pressure variable-temperature measurements are telling us about ion transport in glass.
Dalton Transactions, vol. 2004, no. 19, pp. 3067-3070Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b403427a
The concept of matrix-mediated coupling: a new interpretation of mixed-cation effects in glass
Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, vol. 15, no. 16, pp. S1595-S1605Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/15/16/309
Application of complementary experimental techniques to characterization of the phase behavior of [C(16)mim][PF6] and [C(14)mim][PF6]
Chemistry of Materials, vol. 15, pp. 3089-3097Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cm021378u
Effect of pressure on ion transport in amorphous and semi-crystalline polymer electrolytes
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 395-399Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b208552f
Band gaps and refractivity of silicates: A chemical approach to UV absorption of glass
Comptes Rendus Chimie, vol. 5, pp. 797-804Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1631-0748(02)01448-0
Ion transport in hydrated sodium slicates (water glasses) of varying water content
Solid State Ionics, vol. 146, pp. 113-122Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(01)00990-0
Pressure dependent conductivities and activation volumes in LixNa(1-x)PO3 glasses: evidence for a new matrix-mediated coupling mechanism in mixed-cation glasses?
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, vol. 4, pp. 3209-3213Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b201215d
Decoupled ion transport in mesomorphis polymer electrolyte glasses
Electrochimica Acta, vol. 46, no. 10-11, pp. 1413-1417Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00734-9
Bridging the gap between polymer electrolytes and inorganic glasses: Side group liquid crystal polymer electrolytes
Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, vol. 347, no. 1, pp. 199-210Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10587250008024841
Ion transport in glassy polymer electrolytes
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 103, pp. 4132-4138Contributions to Journals: ArticlesIon transport in glassy side-group liquid crystalline polymer electrolytes
Advanced Materials Research, vol. 11, no. 10, pp. 832-834Contributions to Journals: ArticlesFrom Simple Electrolyte Solutions Through Polymer Electrolytes to Superionic Rubbers: Some Fundamental Considerations
Polymer International, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 9-15Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Ionically conducting side chain liquid crystal polymer electrolytes
Electrochimica Acta, vol. 43, no. 10-11, pp. 1151-1154Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(97)10013-5
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
