The Aberdeen Streaming Potential Apparatus (ASPA) is suited for single- and multi-phase (unsteady state) fluid displacement in porous media experiments, combined with the streaming potential (zeta potential) measurements. The setup comprises core holders (PVC and PEEK, operating at T < 150C, P <10 MPa), pressure transducers, custom non-polarising electrodes, National Instruments data acquisition system, desktop computer with licenced LabView, QUADTECH 7600 Plus Precision LCR meter, oven, ISCO and GDS pumps.

ASPA: The experimental apparatus used in streaming potential measurements (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.076). The solid grey lines represent flowlines and the dashed grey lines represent electrical connections. (#1) heated Hastelloy ISCO pumps; (#2) GDS Flow-Pressure Controller pump used to induce the confining pressure around the rock sample; (#3) PS and National Instruments data acquisition system; (#4) core holder (suitable for HPHT); (#5) two high precision pressure transducers; (#6) pressure transducer for monitoring the confining pressure; (#7) custom external Ag/AgCl; (#8) internal Ag/Ag/Cl electrodes; (#9) sampling tubes; (#10) CO2 cylinder (optional); (#11) stainless steel ISCO pump for pumping CO2 into the mixing reactor (optional); (#12) heated Parr mixing reactor (optional); (#13) high pressure in-line pH meter (optional).
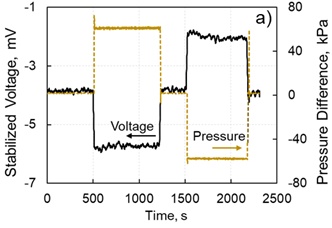
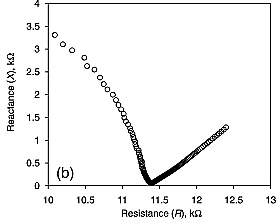
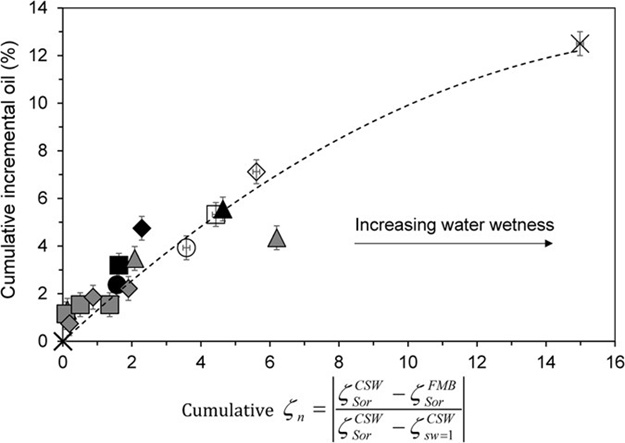
Fluid is pumped through a porous sample inside the core holder until pressure difference and voltage stabilise (plot a below; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.076). From the stabilised values of pressure and voltage, the zeta potential is interpreted using the sample’s electrical conductivity which is interpreted from measured reactance and total impedance to applied AC voltage swept over the frequency range of 10 Hz to 2 MHz (plot b below; https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB007593). In case of a multi-phase experiment (two immiscible fluids reside in the sample simultaneously), fluid phase saturation is evaluated from the volume balance (i.e., injected volumes of immiscible fluids are compared with the produced volumes), and the measured multi-phase zeta potential is correlated with the phase saturation (plot c below; https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37363).